NEW DELHI: India's school system has recorded one of its sharpest gains in recent years, with dropout rates falling significantly across all levels, according to the ministry of statistics and programme implementation's (MoSPI) Comprehensive Modular Survey: Education, 2025.
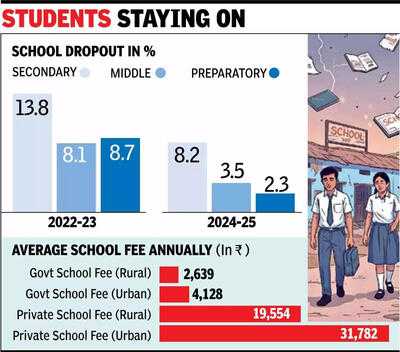
The survey, conducted during April-June 2025 as part of the 80th round of the National Sample Survey, shows that dropout rates have nearly halved within just two years. At the secondary level, the rate fell to 8.2% in 2024-25 from 13.8% in 2022-23. At the middle level, it dropped to 3.5% from 8.1%, while at the preparatory stage, it declined to 2.3% compared with 8.7% earlier.
This sharp improvement signals a structural turnaround in retention, suggesting that more children are staying enrolled and completing schooling. Experts link the gains to govt initiatives such as expanded mid-day meals, targeted scholarships for disadvantaged groups, better infrastructure under Samagra Shiksha Abhiyan, and the flexibility introduced by the National Education Policy (NEP-2020).
Yet the survey also uncovers a nuanced challenge around affordability. While more children are completing school, household spending on education has risen steadily. In rural India, the average annual expenditure per student on govt schools was Rs 2,639, compared to Rs 19,554 in non-govt schools. In urban areas, the difference is sharper - Rs 4,128 in govt schools against Rs 31,782 in private unaided institutions. Overall, 57% of students reported paying course fees, with the proportion much higher in private schools.
This suggests that families are stretching finances to sustain education, even as retention improves. "Improved retention is a success, but sustaining it requires keeping education affordable. Rising costs could become the next barrier, particularly for low-income families," said an official with the ministry of education.
The steepest improvements were seen at the preparatory and middle levels, long considered vulnerable to socio-economic pressures. That these stages now show the lowest dropout levels is being read as proof that early interventions are paying off. But the secondary stage remains fragile, where adolescents face competing demands: household income, early work, and the absence of nearby higher-secondary schools.
A MoSPI official noted, "India is steadily moving towards ensuring that every child not only enters but also completes school. The challenge now is sustaining retention at the secondary stage, where aspirations often collide with financial realities."
The MoSPI report is particularly significant because it provides fresh national-level estimates after a seven-year gap, offering policymakers vital evidence for India's push towards universal secondary education and higher Gross Enrolment Ratios. Experts argue that if the current downward trend in dropouts continues, India could achieve near-universal school completion within a decade, provided affordability and access remain central to reforms.
The survey, conducted during April-June 2025 as part of the 80th round of the National Sample Survey, shows that dropout rates have nearly halved within just two years. At the secondary level, the rate fell to 8.2% in 2024-25 from 13.8% in 2022-23. At the middle level, it dropped to 3.5% from 8.1%, while at the preparatory stage, it declined to 2.3% compared with 8.7% earlier.
This sharp improvement signals a structural turnaround in retention, suggesting that more children are staying enrolled and completing schooling. Experts link the gains to govt initiatives such as expanded mid-day meals, targeted scholarships for disadvantaged groups, better infrastructure under Samagra Shiksha Abhiyan, and the flexibility introduced by the National Education Policy (NEP-2020).
Yet the survey also uncovers a nuanced challenge around affordability. While more children are completing school, household spending on education has risen steadily. In rural India, the average annual expenditure per student on govt schools was Rs 2,639, compared to Rs 19,554 in non-govt schools. In urban areas, the difference is sharper - Rs 4,128 in govt schools against Rs 31,782 in private unaided institutions. Overall, 57% of students reported paying course fees, with the proportion much higher in private schools.
This suggests that families are stretching finances to sustain education, even as retention improves. "Improved retention is a success, but sustaining it requires keeping education affordable. Rising costs could become the next barrier, particularly for low-income families," said an official with the ministry of education.
The steepest improvements were seen at the preparatory and middle levels, long considered vulnerable to socio-economic pressures. That these stages now show the lowest dropout levels is being read as proof that early interventions are paying off. But the secondary stage remains fragile, where adolescents face competing demands: household income, early work, and the absence of nearby higher-secondary schools.
A MoSPI official noted, "India is steadily moving towards ensuring that every child not only enters but also completes school. The challenge now is sustaining retention at the secondary stage, where aspirations often collide with financial realities."
The MoSPI report is particularly significant because it provides fresh national-level estimates after a seven-year gap, offering policymakers vital evidence for India's push towards universal secondary education and higher Gross Enrolment Ratios. Experts argue that if the current downward trend in dropouts continues, India could achieve near-universal school completion within a decade, provided affordability and access remain central to reforms.
You may also like

Elderly couple who nearly died in Taliban prison hell could return to Afghanistan

Ishaan Khatter remembers early days that gave him ability to understand 'Homebound'

SC bans sale of 'any crackers' in Delhi-NCR until further notice

Brits die every three minutes from silent killer as TV star unveils new campaign to fight

P-Valley star's 'powerful' romantic film quietly added to Netflix






